Manual handling in aged care involves safely lifting, transferring, and positioning residents to maintain their dignity and prevent injuries. It requires careful techniques and equipment to ensure both caregiver and resident safety effectively.

Importance
Proper manual handling is crucial for preventing injuries, promoting residents’ dignity, and ensuring a safe care environment. It reduces physical strain on caregivers and minimizes risks associated with lifting and transferring techniques effectively.

Preventing Injuries
Proper manual handling techniques are essential for preventing injuries to both caregivers and residents. By using correct lifting methods, such as bending at the knees and maintaining a straight back, the risk of strain and musculoskeletal injuries can be significantly reduced. Additionally, the use of assistive equipment like sliding boards or hoists minimizes physical exertion and ensures safe transfers. Assessing the individual needs of each resident allows caregivers to tailor their approach, further reducing the likelihood of accidents. Regular training and adherence to care plans also play a critical role in maintaining safety. When manual handling is performed incorrectly, it can lead to serious harm, making it vital to prioritize proper techniques and equipment. By focusing on injury prevention, caregivers can create a safer environment for both themselves and the residents they support. This approach not only protects physical health but also promotes a culture of care and responsibility.
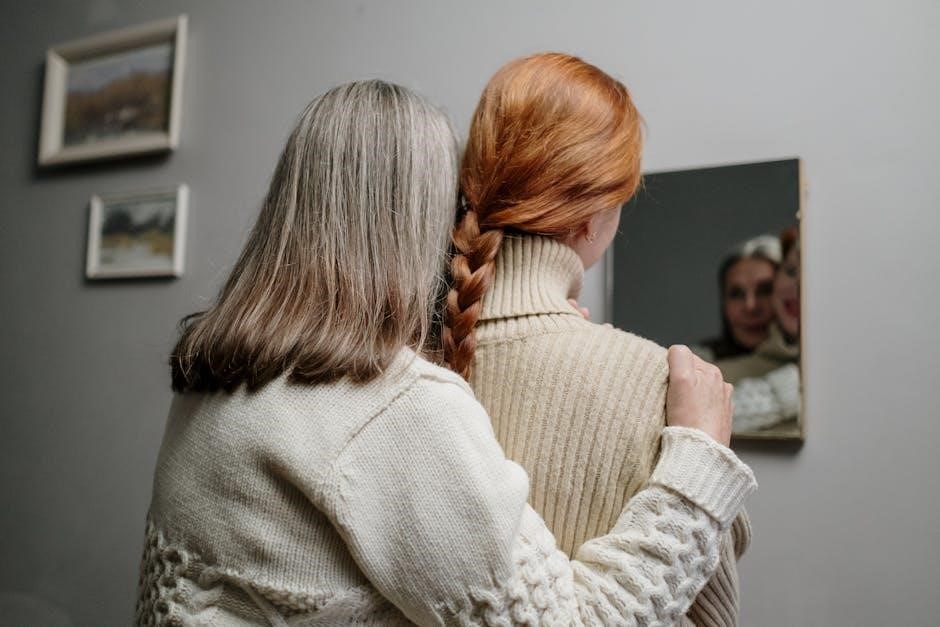
Promoting Dignity
Manual handling in aged care not only focuses on safety but also plays a crucial role in promoting the dignity of residents. Respectful and considerate handling ensures that individuals feel valued and comfortable during transfers or repositioning. Caregivers should always maintain open communication, allowing residents to express their needs and preferences. This approach fosters trust and reduces anxiety, making the experience more positive for everyone involved. Additionally, using appropriate equipment and techniques minimizes the risk of embarrassment or discomfort, which can arise from improper handling. By prioritizing dignity, caregivers contribute to the emotional and psychological well-being of residents, which is as important as their physical care. Ensuring residents feel respected and empowered during manual handling tasks is essential for maintaining their self-esteem and overall quality of life. This balance between safety and dignity is fundamental to providing compassionate and person-centered care in aged care settings.

Risks
Manual handling in aged care poses significant physical risks, including injuries to both caregivers and residents. Improper techniques can lead to musculoskeletal strains, sprains, and fractures, emphasizing the need for proper training and precautions.
Physical Risks
Physical risks associated with manual handling in aged care are significant. Caregivers often experience musculoskeletal injuries, such as back strains or sprains, due to improper lifting techniques or overexertion. Additionally, repetitive tasks like pushing, pulling, or carrying can lead to long-term health issues. Residents are also at risk, as improper handling can result in fractures, bruises, or dislocations. The physical demands of manual handling highlight the importance of proper training and the use of assistive equipment, such as hoists or sliding boards, to minimize these risks. Employers must ensure that caregivers are aware of these dangers and take necessary precautions to protect both themselves and the residents in their care. Regular assessments and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to mitigating physical risks effectively.
Challenges
Manual handling in aged care presents numerous challenges, particularly due to the diverse needs and conditions of residents. One major challenge is the unpredictable nature of residents’ physical conditions, such as limited mobility, weight, or medical frailty, which can complicate lifting and transferring tasks. Additionally, some residents may exhibit behavioral difficulties, such as resistance or anxiety, which can hinder safe handling practices. Caregivers must also contend with environmental factors, such as cramped spaces or lack of appropriate equipment, which can increase the difficulty of manual tasks. Furthermore, the emotional and cognitive challenges of caring for vulnerable individuals can add stress to the process. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of proper training, effective care planning, and the use of specialized equipment to ensure the safety and dignity of both residents and caregivers. By overcoming these obstacles, caregivers can provide high-quality, person-centered care while minimizing risks.

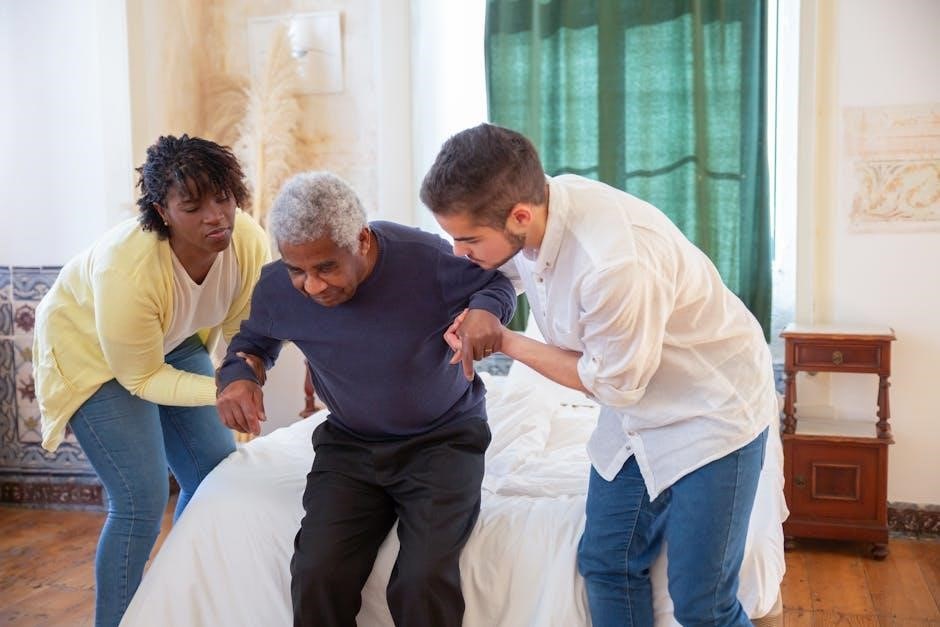
Safe Techniques
Safe manual handling techniques in aged care involve proper lifting, posture, and equipment use. Sliding boards and hoists minimize strain, while maintaining resident dignity and stability ensures safe transfers and positioning always.
Proper Lifting
Proper lifting techniques are essential in manual handling for aged care to prevent injuries and ensure resident safety. Caregivers should bend at the knees, keep the load close to their body, and avoid twisting; Sliding boards or hoists can assist with transfers, reducing physical strain. Residents should be encouraged to support their own weight if possible. Maintaining a stable posture and using leg muscles instead of back strength is crucial. Training programs often emphasize these methods to minimize risks for both caregivers and residents. Proper lifting not only protects against physical harm but also promotes dignity and comfort during care. Regular practice and adherence to guidelines ensure consistent and safe manual handling practices in aged care settings. Proper lifting techniques are fundamental to creating a safe and respectful care environment.
Posture and Positioning
Proper posture and positioning are critical in manual handling for aged care to minimize strain and prevent injuries. Caregivers should maintain a neutral spine alignment, avoiding rounded shoulders or arched backs. When assisting residents, they should encourage upright posture to reduce the risk of falls or discomfort. Positioning techniques, such as standing with feet shoulder-width apart and knees slightly bent, provide stability during transfers. Residents should be positioned to support their balance and mobility, with caregivers guiding rather than lifting. Using assistive devices like canes or walking frames can further enhance stability. Proper posture and positioning not only protect caregivers but also promote residents’ independence and dignity. Regular training and practice help caregivers master these techniques, ensuring safe and effective manual handling in aged care settings. By prioritizing proper posture and positioning, caregivers can create a safer environment for both themselves and the residents in their care.
Use of Equipment
The use of appropriate equipment is essential in manual handling for aged care to ensure safety and efficiency. Devices such as sliding boards, hoists, and stand-up lifts are commonly used to assist with transferring and repositioning residents; Sliding boards are particularly useful for residents with limited mobility, allowing smooth transitions between surfaces like beds and chairs. Hoists provide mechanical support for heavier residents, reducing the physical strain on caregivers. Stand-up lifts enable residents to maintain some independence by supporting them as they stand or move. Proper training is crucial to operate this equipment safely and effectively. Caregivers should always follow manufacturer guidelines and ensure equipment is well-maintained. The right tools not only prevent injuries but also promote dignity and comfort for residents during handling. By incorporating equipment into manual handling practices, caregivers can create a safer and more efficient care environment for both themselves and the individuals they support.

Training
Proper training in manual handling techniques is crucial for caregivers to ensure safety and efficiency. It equips them with skills to lift, transfer, and reposition residents safely, reducing injury risks and promoting effective care practices regularly.
Role in Safety
Training plays a pivotal role in ensuring safety during manual handling in aged care. By equipping caregivers with proper techniques, it significantly reduces the risk of injuries to both residents and staff. Proper training ensures that caregivers understand how to use equipment like hoists and sliding boards effectively, minimizing strain and preventing accidents.
Moreover, trained caregivers can assess individual resident needs, adapting their approach to accommodate mobility limitations or medical conditions. This personalized care not only enhances safety but also promotes dignity and comfort for the residents. Regular training updates and refreshers are essential to maintain high standards of safety and adapt to new techniques or equipment in the field of aged care.
Ultimately, the role of training in safety cannot be overstated. It empowers caregivers to provide compassionate and effective care while safeguarding against potential hazards, creating a safer environment for everyone involved.
Code of Practice
The Code of Practice for manual handling in aged care provides a framework of guidelines to ensure tasks are performed safely and ethically. It outlines the responsibilities of caregivers, employers, and organizations to minimize risks associated with manual handling. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments, using appropriate equipment, and adhering to proper lifting techniques.
The code emphasizes the importance of balancing safety with the dignity and comfort of residents. It requires caregivers to be trained in handling techniques and to use assistive devices when necessary. Employers must provide a safe working environment, ensure equipment is well-maintained, and promote a culture of safety within the organization.
By following the Code of Practice, aged care facilities can reduce the likelihood of injuries to both residents and staff. It serves as a foundational document to guide decision-making and ensure that manual handling tasks are carried out with care, respect, and professionalism.

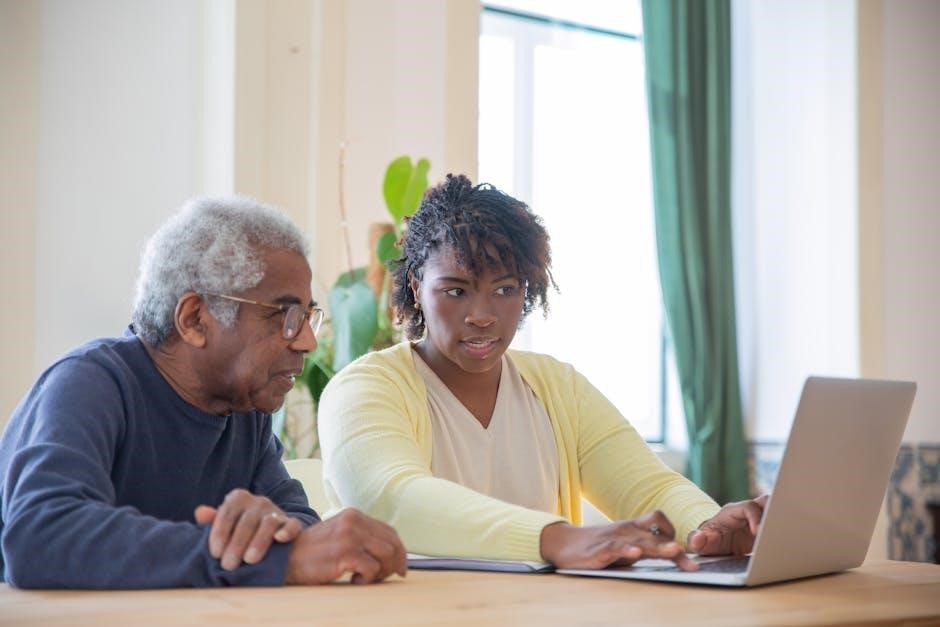
Assessment
Assessment in manual handling for aged care involves evaluating the specific needs of residents to ensure safe and effective care. Individual assessments help identify risks and develop personalized care plans to minimize harm and promote well-being.
Individual Assessments
Individual assessments are crucial in manual handling for aged care, focusing on the unique needs and capabilities of each resident. These evaluations consider factors such as mobility, strength, and medical conditions to determine the safest methods for lifting, transferring, and repositioning. By understanding each resident’s specific requirements, caregivers can minimize the risk of injury to both the resident and themselves. The assessment process often involves input from healthcare professionals, including physiotherapists and occupational therapists, to create personalized care plans. This tailored approach ensures that manual handling techniques are adapted to the individual, promoting independence and dignity while maintaining safety. Regular reassessments are necessary to accommodate changes in a resident’s condition or abilities, ensuring ongoing safety and effectiveness in care delivery.
Care Planning
Care planning is a critical component of manual handling in aged care, ensuring that individualized strategies are developed to meet the unique needs of each resident. This process involves creating a detailed plan that outlines the safest methods for lifting, transferring, and repositioning, based on the results of individual assessments. The plan is tailored to the resident’s specific abilities, medical conditions, and personal preferences, with the goal of promoting independence and dignity. Care plans are typically developed in collaboration with the resident, their family, and healthcare professionals, ensuring a holistic approach. They include specific goals, such as improving mobility or reducing the risk of falls, and outline the use of appropriate equipment or assistive devices. Regular reviews and updates to the care plan are essential to reflect any changes in the resident’s condition or care requirements, ensuring ongoing safety and effectiveness in manual handling practices.


Teamwork
Teamwork is essential in manual handling for aged care, as it ensures the safe and effective movement of residents. When caregivers work together, they can share the physical demands of manual handling, reducing the risk of injury to both staff and residents. Effective communication and coordination are key, enabling the team to anticipate and respond to the resident’s needs seamlessly. Teamwork also promotes a supportive environment, where each member can contribute their strengths and expertise, enhancing overall care quality. By collaborating, caregivers can use appropriate techniques and equipment, such as sliding boards or hoists, more efficiently. Regular training and team meetings help foster a culture of safety and cooperation, ensuring that everyone is aligned in their approach to manual handling. Strong teamwork not only improves safety but also enhances the dignity and comfort of residents, making it a cornerstone of effective aged care practices.

Legal
Manual handling in aged care must comply with legal standards to protect both caregivers and residents from injuries. Laws regulate safe practices, and non-compliance can lead to legal consequences.
Regulations
Regulations governing manual handling in aged care are designed to ensure safety and compliance. Laws such as the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 in the UK require employers to assess risks and implement safe practices. Employers must conduct thorough risk assessments, provide proper training, and ensure equipment is available. These regulations aim to protect both caregivers and residents from injuries. Penalties for non-compliance can be severe, emphasizing the importance of adherence. Additionally, international standards and local laws may impose further requirements tailored to specific regions. Compliance with these regulations is essential for maintaining legal and ethical standards in aged care settings.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers in aged care settings are responsible for ensuring a safe working environment and protecting both staff and residents from manual handling risks. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments, providing appropriate training, and ensuring that proper equipment is available and maintained. Employers must also supervise staff to ensure safe practices are followed consistently. Additionally, employers are obligated to provide personal protective equipment (PPE) where necessary and to maintain accurate records of training and incidents. Regular reviews of manual handling procedures are essential to adapt to changing needs and ensure compliance with legal standards. Employers who fail to meet these responsibilities may face legal consequences and jeopardize the well-being of their employees and residents. By prioritizing safety, employers can create a culture of care and responsibility within their organizations.